Process menu:
This will bring up:
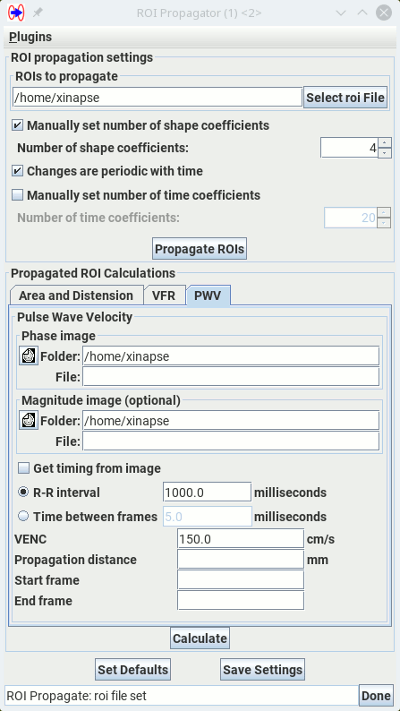
The ROI Propagation tool is used to propagate ROIs that change slowly over time or space. A set of ROIs is defined at one or more time points in (typically) a cine image, outlining certain features of the image that are of interest. The tool can then fill in any gaps between time points where the ROIs have not been defined, or extrapolate them over the whole time course.
You can constrain the propagation so that the ROIs propagate smoothly, and you can also enforce periodicity so that there is a smooth transition from the end of the time course back to the beginning, as should be the case when propagating through a cardiac cycle.
When the propagation is complete, there are tools to perform further analysis using the ROIs; these tools are typically what is needed for cardiac-related analysis, but you can also easily write your own tool using the Java programming language, and load it as a plugin into the ROI Propagation tool.
Start the ROI Propagation tool from the Process menu:

This will bring up:
When drawing the outlines, you can use:
Note: at the time points where you have defined the ROIs, the propagated ROIs will not be exactly the same as the ones you have defined, because the tool will attempt to make the ROIs follow the outlines of shapes as precisely as possible.
When you have defined the ROIs at your chosen time points, save the ROIs to a disk file.
Options that influence the ROI propagation are described in the processing options section.